CloudLingo-A-Serverless-Language-Translator-with-AWS-Translate-and-Lambda
🌍 CloudLingo: A Serverless Language Translator with AWS Translate and Lambda
Author: Bernard Kwame Solodzi
Date: 2025-09-01
📌 Features
- 🚀 Event-driven workflow – S3 triggers Lambda on file upload.
- 🌐 Multi-language support – Uses Amazon Translate to translate text into Arabic, Spanish, Japanese (and more if configured).
- 📂 Automated output naming – Input
file.json→ Outputfile-output.json. - ☁️ Fully serverless – No servers to manage, pay-per-use model.
Introduction
CloudLingo is an automated translation pipeline using AWS services. JSON files containing text are uploaded into an S3 Request Bucket, which triggers a Lambda function. The Lambda reads the file, uses Amazon Translate to convert the text into the target language, and stores the translated output in an S3 Response Bucket.
This project demonstrates event-driven architecture on AWS to solve real-world problems, eliminating manual translation and enabling automated, scalable, and cost-effective multilingual support.
🏗️ Architecture
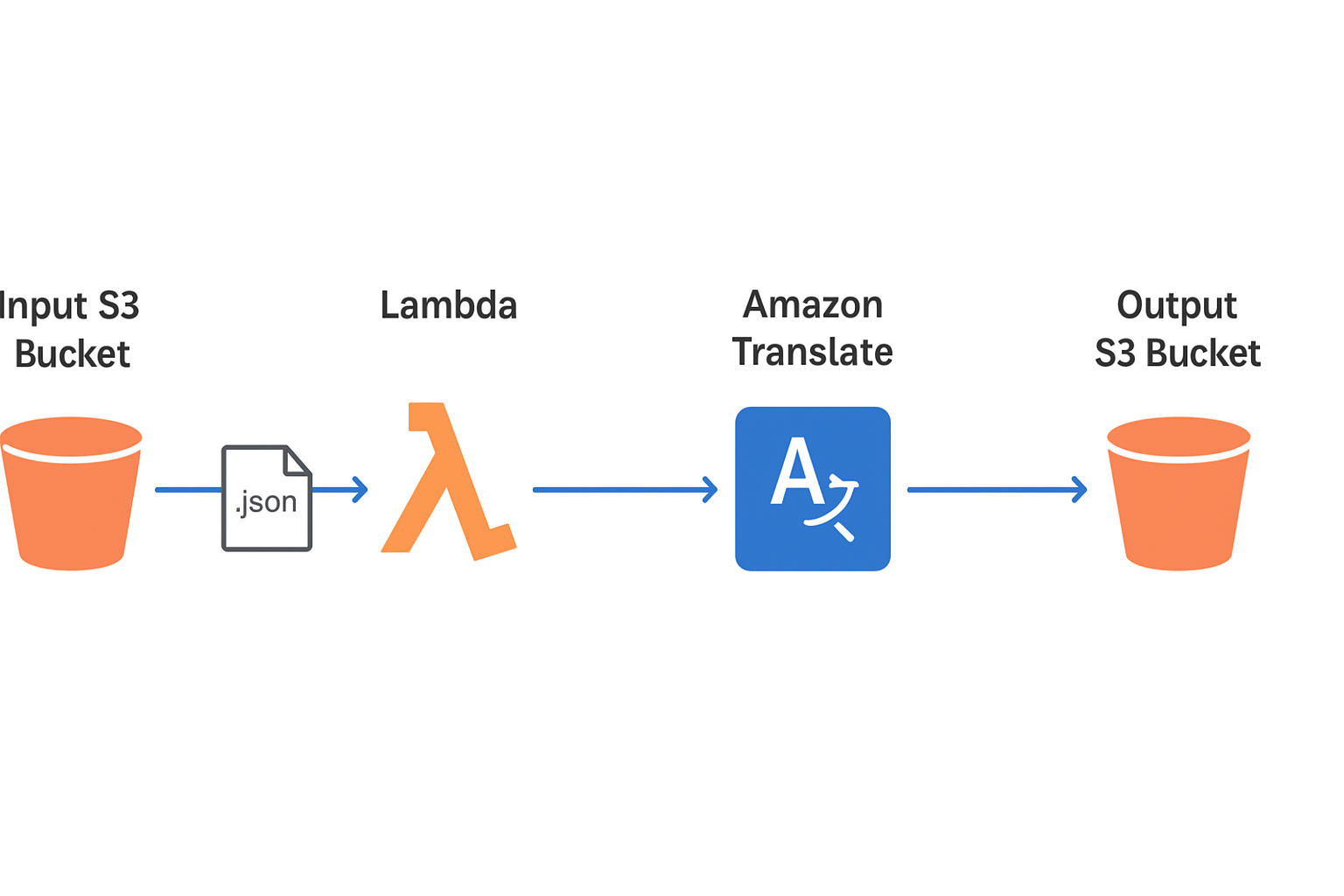
Flow:
- A JSON file is uploaded to the Input S3 Bucket.
- S3 Event Notification triggers the Lambda function.
- The Lambda function:
- Reads the file.
- Sends text to Amazon Translate.
- Stores translated results in the Output S3 Bucket.
- The output file is saved as
filename-output.json.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Architecture
- Prerequisites
- Objectives
- Step 1: Deploy Resources with CloudFormation
- Step 2: Review IAM Role and Policies
- Step 3: Lambda Function Configuration
- Step 4: Test the Translation Pipeline
- Monitoring
- Challenges and Lessons Learned
- Conclusion
- References
Prerequisites
Ensure the following are installed:
- AWS CLI
- Python 3.9+
- AWS credentials configured via
aws configure
Objectives
- Automate S3-triggered Lambda-based translation using AWS Translate.
- Use CloudFormation to create:
- S3 buckets with lifecycle policies
- Lambda execution role with scoped IAM permissions
- Lambda deployment from zip file
- S3 event notification trigger for Lambda
- Package and deploy Python-based Lambda zip
- Log outputs to CloudWatch
- Save translated files into a different S3 bucket
Step-by-Step Guidelines
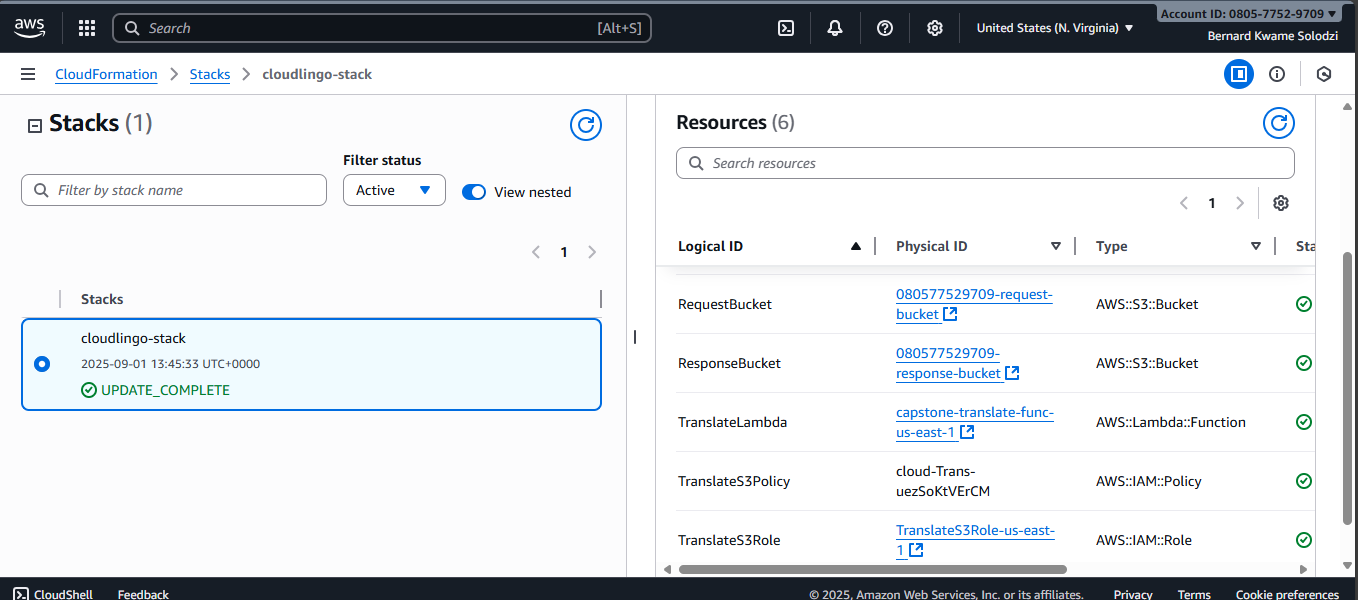
Step 1: Deploy Resources with CloudFormation
All scripts and templates used in this project are openly available in this repository, feel free to use all files to reproduce this project.
- Use the provided CloudFormation template (
translation-setup-with-lambda.yaml) to provision all required AWS resources:- S3 Request Bucket (input)
- S3 Response Bucket (output)
- Lambda function
- IAM roles and policies
- S3 event notification trigger
-
In the AWS Console, go to CloudFormation → Create stack → Upload a template file.
- Follow the prompts to deploy the stack.
- You can review and customize parameters (bucket names, Lambda environment variables, etc.) as needed.
Step 2a: Review IAM Role and Policies
- The CloudFormation template creates an IAM Role for Lambda with:
- AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
- Custom inline policy for:
s3:GetObject,s3:PutObject,s3:ListBuckettranslate:TranslateText
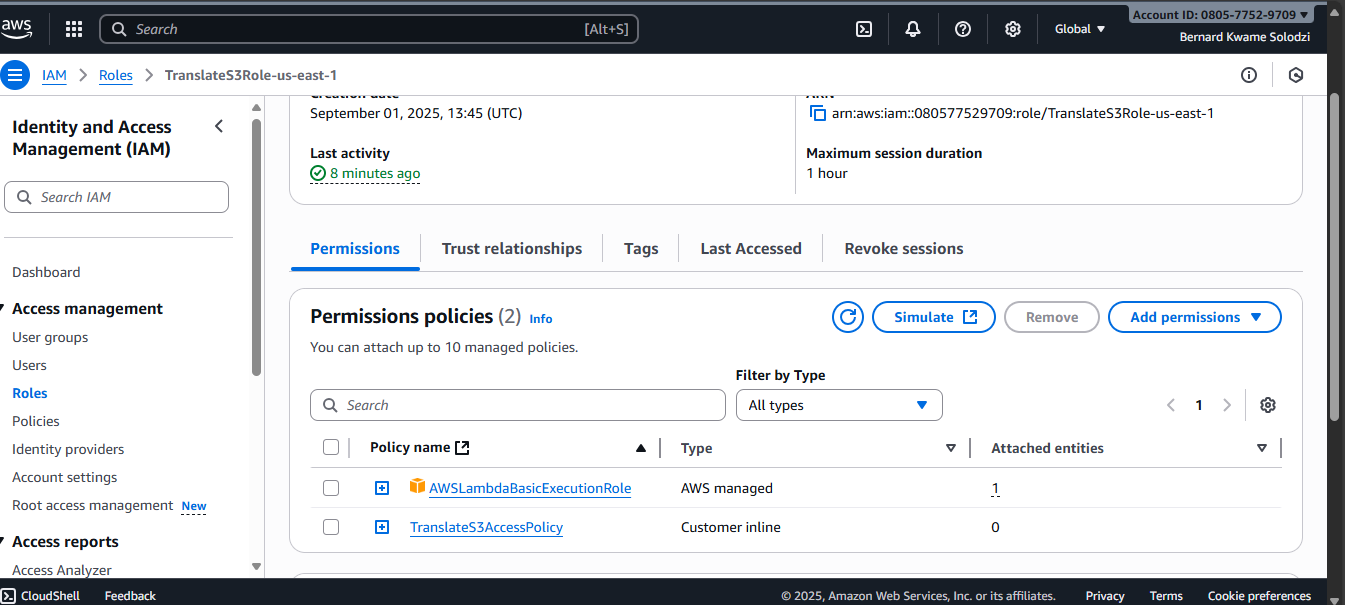
- After deployment, review the IAM role in the AWS Console and adjust permissions if you need additional access.
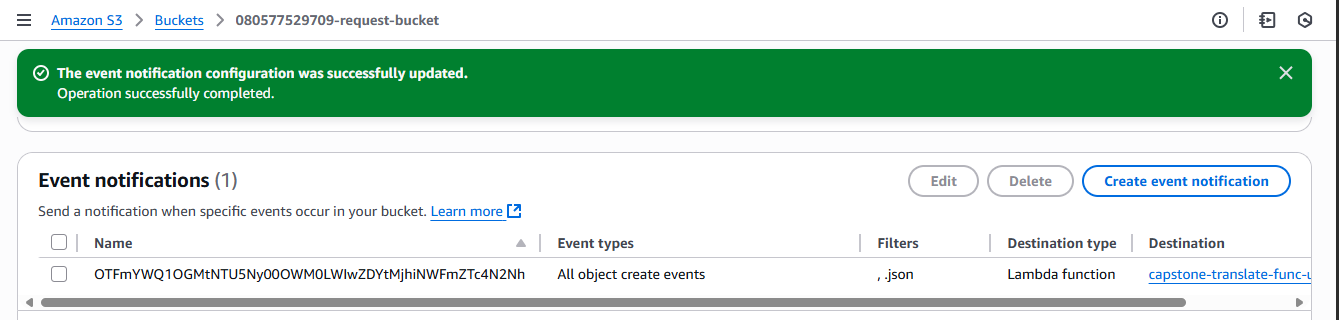
Step 2b: Review the Request S3 bucket to be sure the an s3 event notification event was properly configured as shouw below
Step 3: Lambda Function Configuration
- The Lambda function is provisioned by CloudFormation.
- Runtime: Python 3.12
- Code:
lambda.py(translation logic).
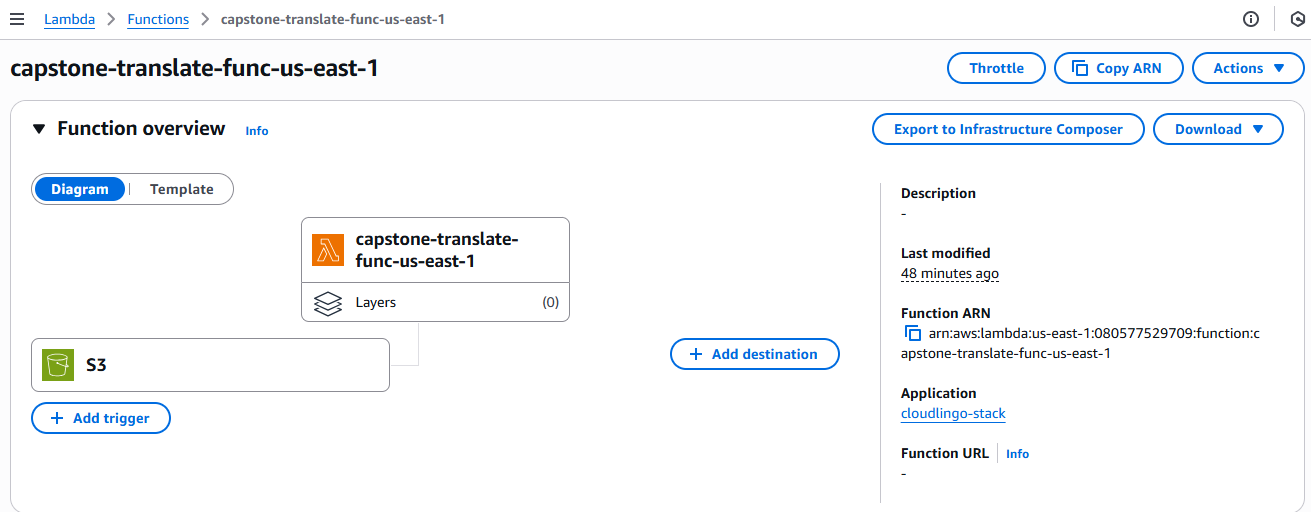
- You can update the Lambda code or environment variables directly in the AWS Console or by updating the CloudFormation stack.
Step 4: Test the Translation Pipeline
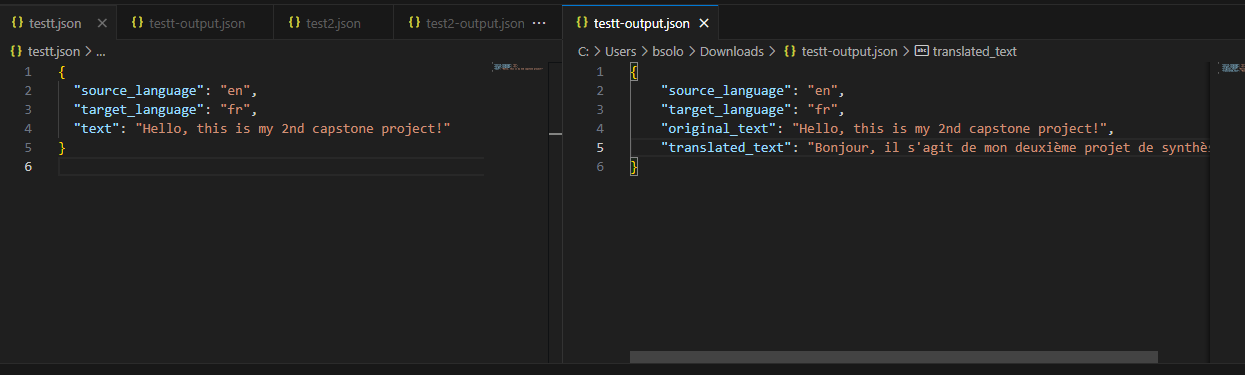
- Upload a JSON file in the format below into the Request Bucket:
{
"source_language": "en",
"target_language": "fr",
"text": "Hello, this is my 2nd capstone project, this is from lambda!"
}
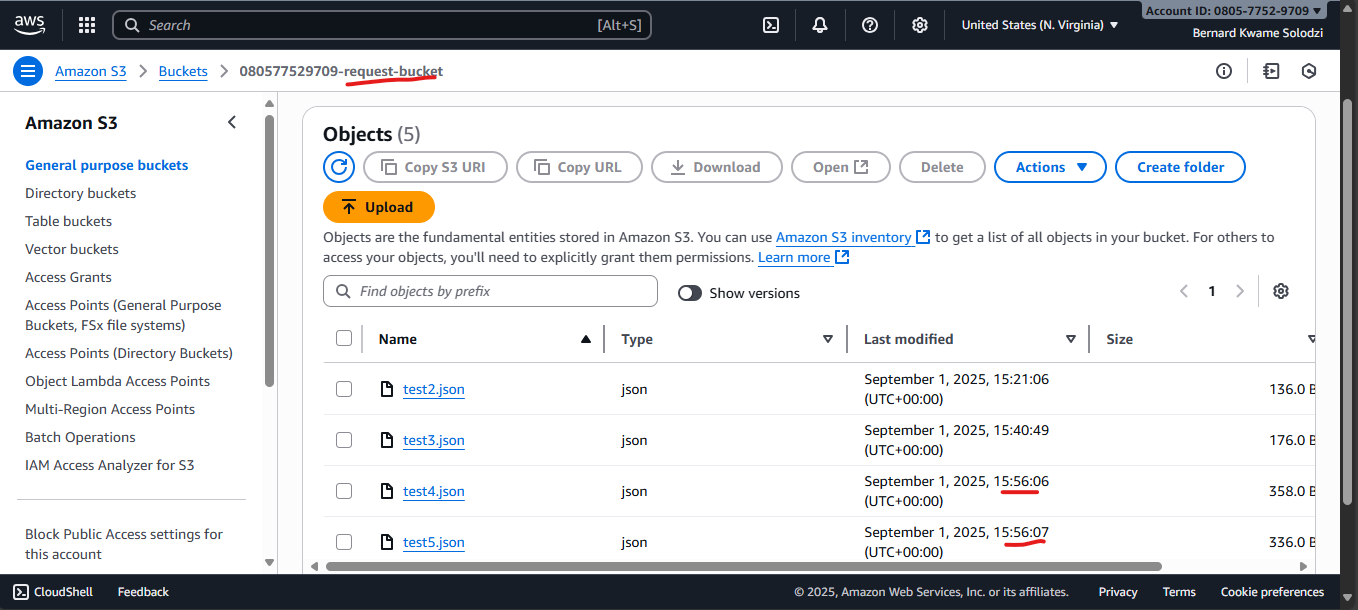
- Check the Response Bucket for an output file (e.g.,
test-output.json):
{
"source_language": "en",
"target_language": "fr",
"original_text": "Hello, this is my 2nd capstone project, this is from lambda!",
"translated_text": "Bonjour, c'est mon deuxième projet de synthèse, il vient de Lambda!"
}
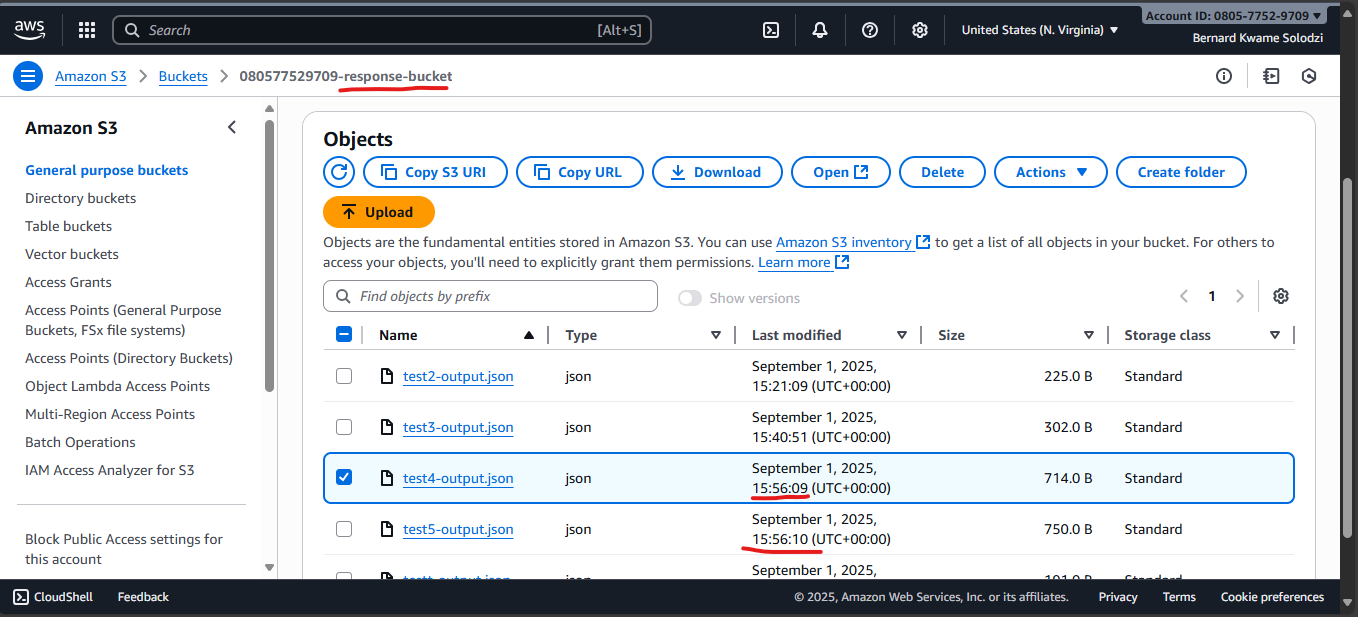
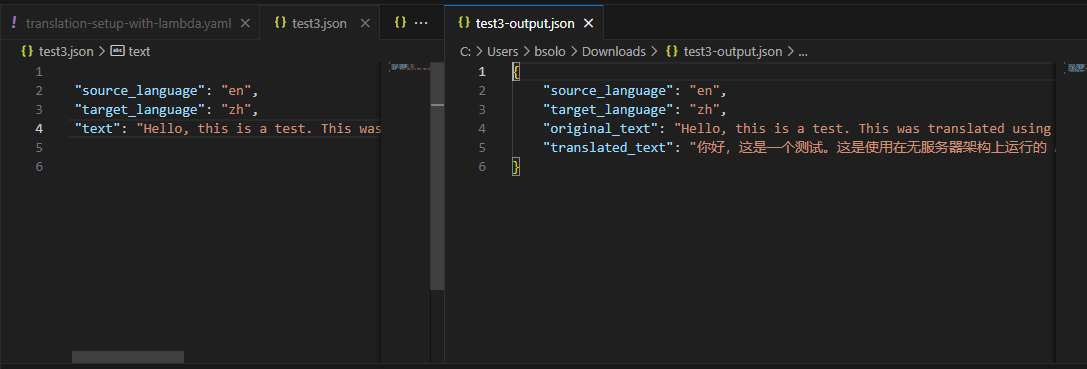
Another Test
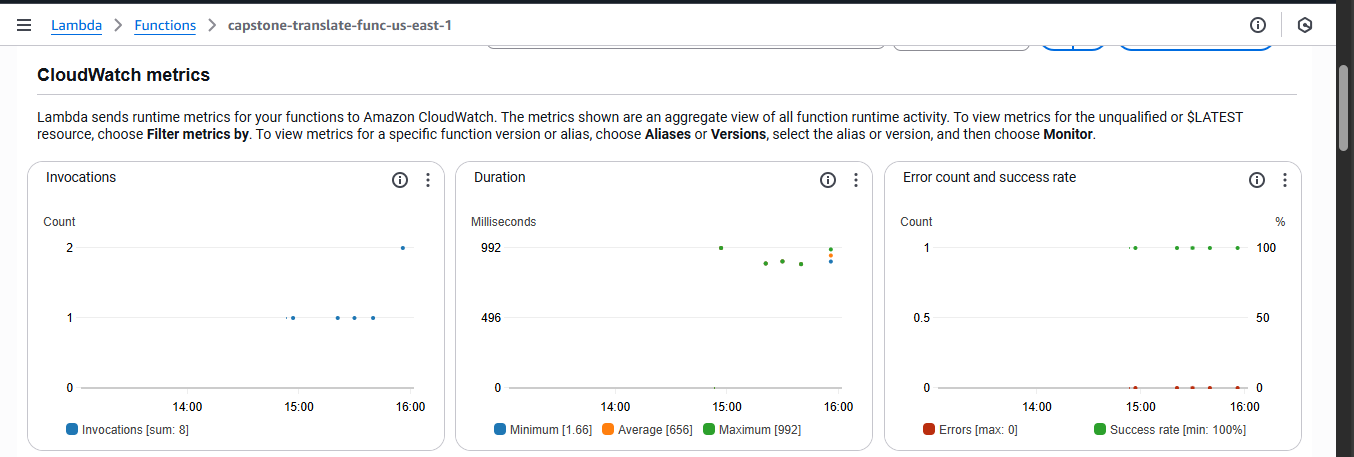
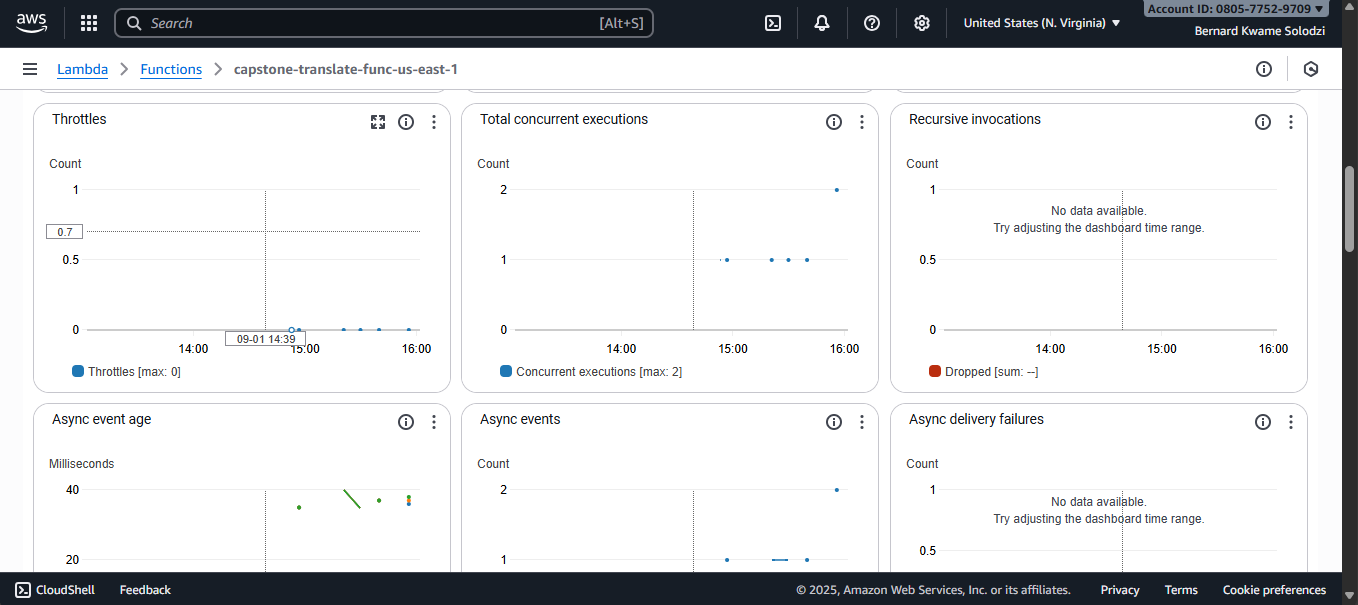
Monitoring
Metrics on Lambda Function
Metrics from AWS Translate Dashboard
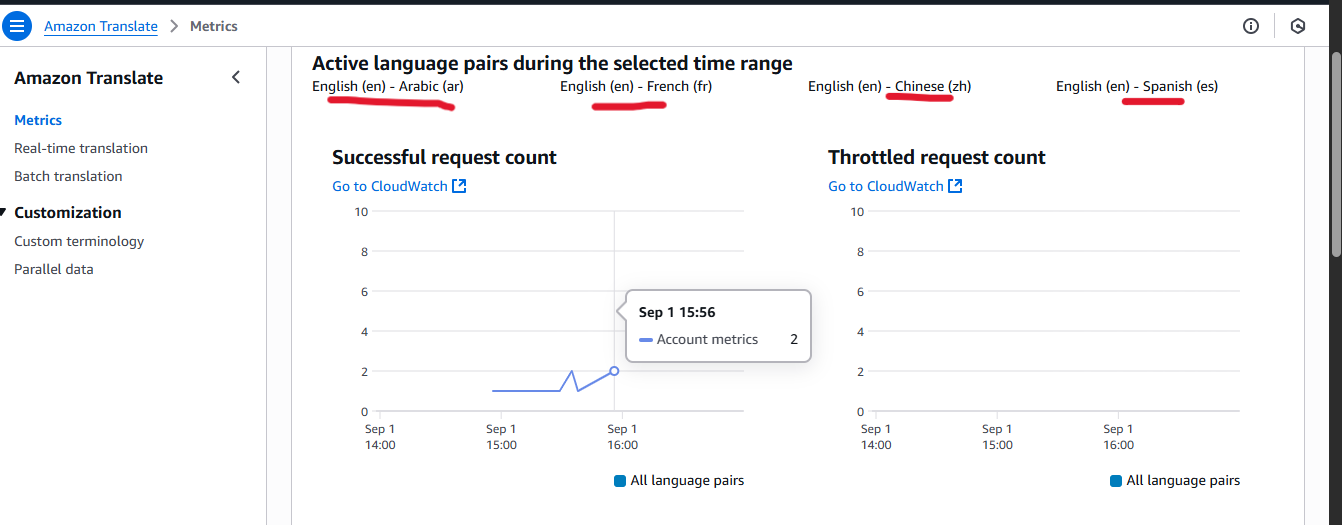
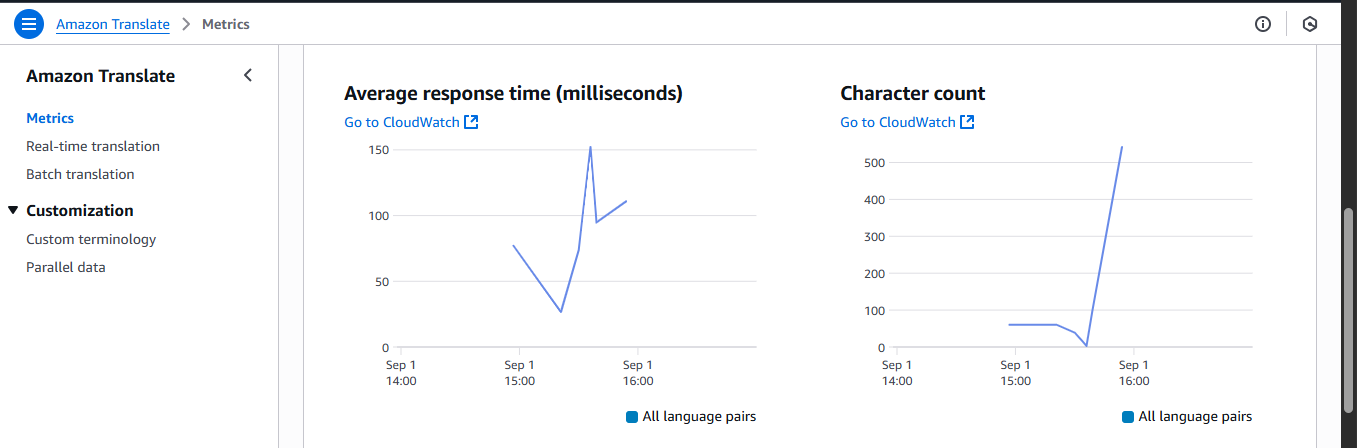
Challenges and Lessons Learned
- Challenge: Ensuring Lambda had the correct IAM permissions to access both S3 buckets and Translate.
- Troubleshooting: Debugging with CloudWatch logs helped identify permission errors and fix JSON parsing issues.
- Lesson Learned: Properly structuring the input/output JSON files is crucial for batch processing and future scalability.
Conclusion
This project demonstrates how AWS serverless services can work together to create an automated translation system. With S3 for storage, Lambda for processing, and Translate for language conversion, CloudLingo provides a scalable, cost-effective, and event-driven pipeline. It eliminates manual translation steps and makes it easy to support multilingual workflows in real time.